Electronic Drilling Recorder (EDR) Systems & Integration of SRD Drilling Mud Sensor
What is the purpose of this article?
This article aims to explain how Electronic Drilling Recorder (EDR) systems work and how Rheonics SRD Drilling Mud Sensor can be integrated into EDR platforms. It provides an overview of common EDR systems, communication protocols (like Modbus, WITS, and WITSML), and describes how real-time sensor data can be transmitted, visualized, and stored both locally and in the cloud for drilling operations.
What products are involved?
An Electronic Drilling Recorder (EDR) or rig data recorder is a system that collects, processes, visualizes, records, and transmits real-time drilling parameters from sensors and rig instrumentation. Typical measured variables include weight on bit (WOB), torque, rotary speed, rate of penetration (ROP), pump pressures, flow rates, choke pressures, mud properties, hook load, downhole sensors, etc.
A modern EDR is often a networked system with local data acquisition, human–machine interface (HMI) displays on the rig floor, and connectivity (edge/cloud) to remote operations centers, often via WITS, WITSML, Modbus, or other data protocols.
One emerging enhancement is the integration of drilling mud property sensors, such as the SRD Inline density meter and viscometer, into the EDR data stream, allowing for continuous, real-time monitoring of mud density and viscosity rather than relying solely on manual lab checks.
1. Commercial EDR / Rig Instrumentation Systems
Below is a list of EDR systems or platforms, with short descriptions and notes on potential integration.
2. How to Connect SRD Sensor to EDR Systems?
Each Electronic Drilling Recorder (EDR) system has its own methodology and configuration procedure for integrating Modbus-based sensors into a WITS (Wellsite Information Transfer Specification) network. The exact steps can vary depending on the EDR manufacturer, software version, and the available communication interfaces. Typically, this process involves defining the Modbus device, mapping registers to the appropriate drilling parameters, and assigning WITS record types or channels for data transmission.
When integrating Rheonics sensors (such as SRD or SRV models) into an EDR system, the following common configuration settings are generally applicable:
2.1. Sensor Settings
The default configuration of the SME-TRD(Modbus RTU) using Modbus can be found in Table 1 below. The configuration can be modified using the RCP software (Figure 1).
| Modbus Communication Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Slave ID | 1 (User configurable) |
| BaudRate | 38400 (User configurable) |
| Parity | odd (User configurable) |
Table 1. Modbus default configuration parameters |
|
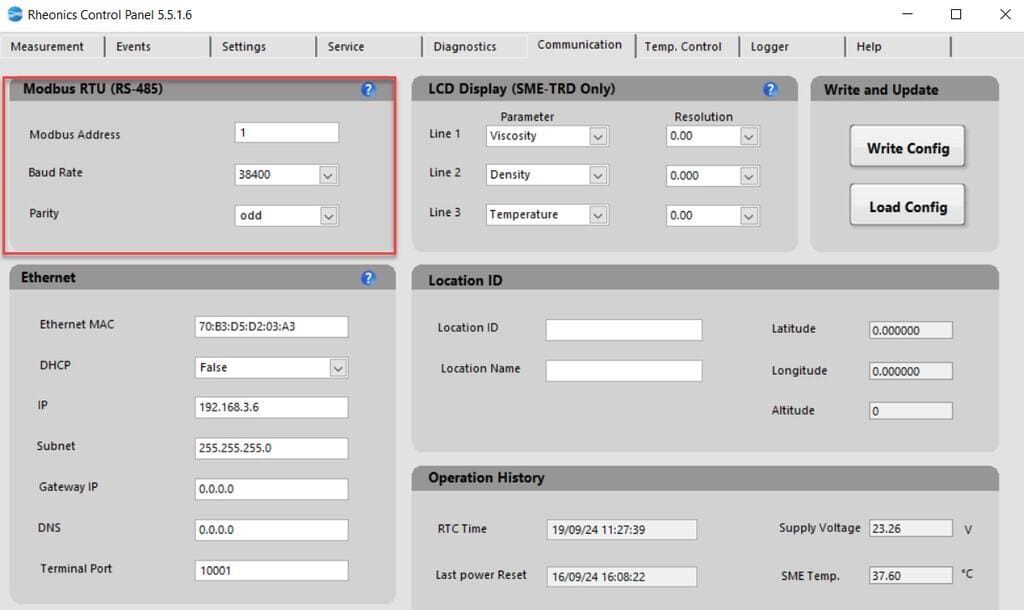
Rheonics sensor can also be configured to use Modbus TCP.
2.2. Recommended registers:
Sensor data is available in the input registers. The table below shows the commonly used registers.
| Parameter 12 | Viscosity Last Good | |||
| 136 | 300137 | 2 | Float32 | Parameter 12 value as float |
| Parameter 13 | Density Last Good | |||
| 144 | 300145 | 2 | Float32 | Parameter 13 value as float |
| Parameter 2 | Temperature median | |||
| 56 | 300057 | 2 | Float32 | Parameter 2 value as float |
3. What is WITS/WITSML?
Wellsite Information Transfer Specification (WITS) is an industry-standard format used for the transmission of wellsite data between computer systems at a drilling rig. It enables real-time data exchange between sensors, rig instrumentation, and data recording systems.
Most Electronic Drilling Recorders (EDRs) support the WITS standard natively, allowing integration with third-party sensors and monitoring systems. When direct compatibility is not available, specialized communication gateways (such as Modbus-to-WITS or OPC-to-WITS converters) can be used to translate and transmit the data in WITS format, enabling interoperability across different hardware and software platforms at the rig site.
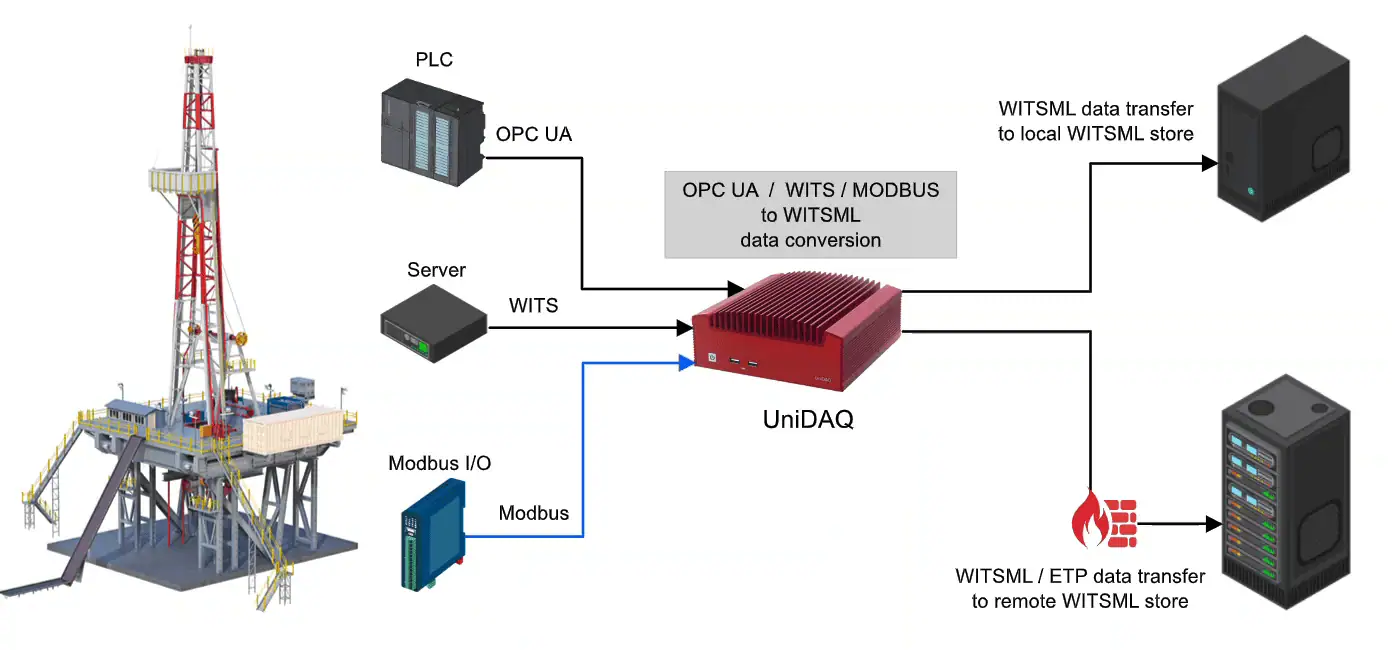
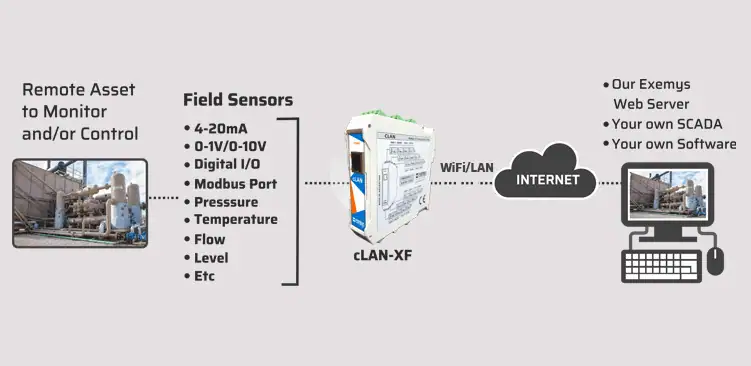
3.1. Specialized gateways
4. Commercial Cloud storage services
Rigsite cloud storage services provide a secure, centralized platform for managing data collected from drilling, completion, and production operations. These services are designed to handle the high-volume, high-frequency data generated at wellsites.
